What are hemorrhoids, and what causes them?
Hemorrhoids, also known as piles, are swollen veins located in the lower rectum or anus. In the United States, hemorrhoids are the third most common outpatient gastrointestinal diagnosis with nearly 4 million office and emergency department visits annually. Hemorrhoids can be internal (inside the rectum) or external (under the skin around the anus).
The exact cause of hemorrhoids is not clear, but certain factors may increase the risk of developing them. These include:
- Straining during bowel movements due to constipation
- Chronic diarrhea or loose stools
- Sitting for long periods, especially on the toilet
- Obesity or being overweight
- Pregnancy, which can put pressure on the veins in the lower abdomen
- Aging, as the tissues supporting the veins in the rectum and anus may weaken over time
Other factors that may contribute to the development of hemorrhoids include a family history of hemorrhoids, a sedentary lifestyle, and a low-fiber diet. Hemorrhoids are a common condition and can occur in people of all ages, but they are more common in adults over the age of 50.
How many types of hemorroids are there?
There are two main types of hemorrhoids: internal hemorrhoids and external hemorrhoids.
- Internal hemorrhoids: These hemorrhoids are located inside the rectum and are generally not visible. They can cause bleeding during bowel movements and may cause a feeling of fullness or discomfort.
- External hemorrhoids: These hemorrhoids are located under the skin around the anus and are visible. They can cause itching, pain, and swelling, and may form blood clots, which can be very painful.
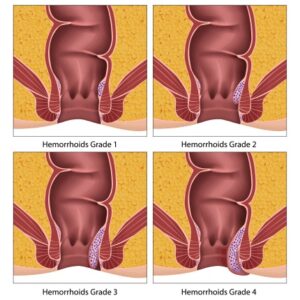
Hemorrhoids can also be classified based on the degree of severity. The four grades of hemorrhoids include:
- Grade 1: The hemorrhoid does not protrude from the anus and is usually painless.
- Grade 2: The hemorrhoid protrudes from the anus during bowel movements but returns to its original position on its own.
- Grade 3: The hemorrhoid protrudes from the anus during bowel movements and must be manually pushed back in.
- Grade 4: The hemorrhoid is always protruding from the anus and cannot be pushed back in.
What are the symptoms of hemorrhoids?
The symptoms of hemorrhoids may vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. Some common symptoms include:
- Itching or irritation in the anal region
- Pain or discomfort during bowel movements
- Bright red blood in the stool, toilet bowl, or on the toilet paper after wiping
- Swelling or a lump around the anus
- Leakage of feces
- Mucus discharge from the anus
Internal hemorrhoids may not cause any symptoms, but when they do, they may cause painless bleeding during bowel movements. External hemorrhoids may cause pain and discomfort, especially when sitting or during bowel movements. Thrombosed hemorrhoids occur when blood clots form in external hemorrhoids and may cause severe pain and swelling.
It is important to note that these symptoms can also be caused by other conditions, such as anal fissures, abscesses, or colon cancer. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan.
How are hemorrhoids diagnosed, and what tests are involved?
The diagnosis of hemorrhoids typically involves a physical examination by a healthcare professional. During the examination, the healthcare professional may perform a visual inspection of the anal region and may also perform a digital rectal exam to check for any abnormalities in the rectum.
In some cases, additional tests may be recommended to rule out other conditions or to confirm the diagnosis of hemorrhoids. These tests may include:
- An anoscopy, which involves using a small, lighted tube to examine the inside of the anus and rectum.
- A sigmoidoscopy or colonoscopy, which involves using a long, flexible tube with a camera to examine the inside of the colon and rectum.
- A stool sample analysis to check for the presence of blood or other signs of infection.
These tests are typically not necessary in cases where the symptoms suggest straightforward hemorrhoids. However, in cases where the healthcare professional suspects another condition or if the patient has risk factors for colon cancer, further testing may be recommended.
What are the available treatment options for hemorrhoids, and which one is right for me?
The treatment options for hemorrhoids depend on the type and severity of the condition. In mild cases, over-the-counter remedies may be sufficient, while more severe cases may require medical or surgical intervention.
Some common treatment options for hemorrhoids include:
- Lifestyle changes: Making dietary and lifestyle changes such as eating a high-fiber diet, drinking plenty of water, and avoiding straining during bowel movements can help alleviate symptoms and prevent hemorrhoids from developing.
- Topical treatments: Over-the-counter creams, ointments, or suppositories containing hydrocortisone or witch hazel can help reduce itching, inflammation, and pain.
- Sitz baths: Soaking the anal area in warm water for 10-15 minutes several times a day can help reduce swelling and relieve discomfort.
- Procedures: In more severe cases, procedures such as rubber band ligation, sclerotherapy, or infrared coagulation may be recommended to shrink or remove hemorrhoids.
- Surgery: In rare cases, surgery may be required to remove large, external hemorrhoids or to correct complications such as excessive bleeding or a blood clot.
The right treatment option for you will depend on the type and severity of your hemorrhoids, as well as your overall health and medical history. It is important to consult a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for your individual needs.
Which is the best cream for hemorrhoids?
There are several over-the-counter creams and ointments available for the treatment of hemorrhoids, and the best cream for you will depend on your specific symptoms and needs. Some common ingredients found in hemorrhoid creams and ointments include:
- Hydrocortisone: This is a corticosteroid that can help reduce itching, inflammation, and swelling associated with hemorrhoids.
- Witch hazel: This is a natural astringent that can help relieve itching and swelling associated with hemorrhoids.
- Lidocaine: This is a local anesthetic that can provide pain relief.
- Phenylephrine: This is a vasoconstrictor that can help reduce swelling and shrink hemorrhoids.
Some popular hemorrhoid creams and ointments include Preparation H, Procto-Synalar, and Anaroid H. It is important to read the label and follow the instructions carefully when using these products. If your symptoms do not improve with over-the-counter treatments, or if you experience persistent or severe symptoms, it is important to consult a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
Can hemorrhoids cause any complications or serious health issues?
In most cases, hemorrhoids are not a serious health concern and can be managed with self-care measures and medical treatment. However, in some cases, hemorrhoids can cause complications or lead to more serious health issues.
Some potential complications of hemorrhoids include:
- Anemia: Chronic bleeding from hemorrhoids can lead to anemia, which is a condition characterized by low levels of red blood cells.
- Strangulated hemorrhoids: If the blood supply to an internal hemorrhoid is cut off, it can become trapped outside the anus and lead to a condition called strangulated hemorrhoid, which can be very painful and require immediate medical attention.
- Thrombosis: External hemorrhoids can develop blood clots, which can be very painful and require medical attention.
- Infection: In rare cases, hemorrhoids can become infected, leading to more serious health issues.
- Colon cancer: Although rare, bleeding from hemorrhoids can mask the symptoms of colon cancer, which is why it’s important to consult a healthcare professional if you experience any bleeding or other symptoms.
While these complications are relatively rare, it is important to seek medical attention if you experience any symptoms of hemorrhoids to prevent any potential complications from developing.
How long does it take for hemorrhoids to heal, and what can I expect during the healing process?
The healing time for hemorrhoids varies depending on the type and severity of the condition, as well as the treatment approach used. In most cases, mild hemorrhoids can be managed with self-care measures and over-the-counter remedies and may resolve within a few days to a week. However, more severe cases may require medical intervention, and healing time may take several weeks.
During the healing process, it is common to experience some discomfort, such as pain, itching, or burning, especially during bowel movements. The use of sitz baths, over-the-counter topical treatments, and pain relievers may help alleviate these symptoms.
If you have undergone a medical or surgical procedure for hemorrhoids, the healing process may take longer. It is important to follow your healthcare professional’s instructions for post-procedure care, including taking any prescribed medications, avoiding heavy lifting, and refraining from strenuous physical activity.
Overall, the healing time for hemorrhoids can vary greatly depending on the individual and the severity of the condition. It is important to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan to help promote healing and alleviate symptoms.
Are there any lifestyle changes or dietary modifications that can help manage hemorrhoids?
Yes, lifestyle changes and dietary modifications can help manage hemorrhoids and reduce symptoms. Some of the changes that may be helpful include:
- Eating a high-fiber diet: A diet high in fiber can help prevent constipation and reduce the risk of hemorrhoids. Foods high in fiber include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes.
- Drinking plenty of fluids: Staying hydrated can help soften stools and prevent constipation.
- Avoiding straining during bowel movements: Try not to strain or push too hard during bowel movements, as this can increase the risk of developing or worsening hemorrhoids.
- Regular exercise: Physical activity can help improve bowel function and prevent constipation.
- Taking breaks from sitting: If you have a sedentary job, try to take breaks from sitting and move around every hour.
- Keeping the anal area clean: After bowel movements, clean the anal area gently with unscented, moistened toilet paper or a wet wipe. Avoid using soap or other harsh cleansers, as these can irritate the area.
- Avoiding irritants: Certain products, such as perfumed toilet paper or soaps, can irritate the anal area and worsen hemorrhoid symptoms. Avoid using these products and opt for unscented, gentle options instead.
- Managing weight: Maintaining a healthy weight can help reduce pressure on the rectum and lower the risk of developing hemorrhoids.
These lifestyle changes may take time to take effect and are most effective when used in combination with other treatments, such as over-the-counter medications, prescription medications, or medical procedures. It is important to talk to a healthcare professional before making any significant changes to your diet or lifestyle to ensure they are safe and appropriate for your individual situation.
When should I seek medical attention for my hemorrhoids, and what are the warning signs of a more serious condition?
You should seek medical attention for your hemorrhoids if you experience persistent symptoms or if over-the-counter treatments are not effective. Additionally, if you have any of the following warning signs, you should seek medical attention immediately, as they may indicate a more serious condition:
- Severe or persistent pain
- Excessive bleeding or blood clots
- Prolapse or protrusion of hemorrhoid tissue outside the anus
- Inability to have a bowel movement
- Rectal bleeding that is not due to hemorrhoids
- Changes in bowel habits or stool color
- Abdominal pain or cramping
- Unexplained weight loss
These symptoms may indicate a more serious condition, such as anal fissures, anal abscesses, inflammatory bowel disease, or colon cancer. It is important to seek medical attention if you experience any of these symptoms to receive an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Do I have to live with hemorrhoids for years?
No, you do not have to live with hemorrhoids for years. Hemorrhoids can be effectively treated with a variety of non-surgical and surgical options. Non-surgical treatments include lifestyle modifications, such as dietary changes and regular exercise, as well as over-the-counter medications and topical creams.
If non-surgical treatments do not provide relief, medical procedures such as rubber band ligation, sclerotherapy, or surgery may be necessary to treat the hemorrhoids. With proper treatment and management, most people with hemorrhoids experience significant improvement in their symptoms and quality of life.
What are the surgical techniques for hemorrhoids?
There are several surgical techniques for treating hemorrhoids, including:
- Hemorrhoidectomy: This is the most common surgical procedure for treating hemorrhoids. It involves removing the hemorrhoidal tissue and is typically used for larger, more severe hemorrhoids.
- Stapled hemorrhoidopexy: This procedure involves using a special stapling device to remove a portion of the hemorrhoid tissue and pull the remaining tissue back into its normal position.
- Doppler-guided hemorrhoidal artery ligation (DGHAL): This procedure involves identifying the blood vessels that supply the hemorrhoids using a special Doppler device and then tying them off to reduce blood flow to the hemorrhoidal tissue.
- Rubber band ligation: This procedure involves placing a rubber band around the base of the hemorrhoid to cut off blood flow and cause the hemorrhoid to shrink and fall off.
- Laser therapy: This procedure involves using a laser to cauterize the blood vessels supplying the hemorrhoid, causing it to shrink and eventually disappear.
The choice of surgical technique depends on the severity and location of the hemorrhoids, as well as the individual’s overall health and medical history. It is important to discuss the options with a qualified healthcare provider to determine the best course of treatment.
What is the difference between hemorrhoids and anal fissures?
Hemorrhoids and anal fissures are both conditions that can cause pain and discomfort in the anal area, but they are two different conditions with distinct symptoms and causes.
Hemorrhoids are swollen veins in the rectum or anus that can cause pain, itching, and bleeding. Hemorrhoids can be internal or external, and they are often caused by straining during bowel movements, pregnancy, or sitting for extended periods.
Anal fissures, on the other hand, are small tears in the skin around the anus that can cause pain and bleeding during bowel movements. Anal fissures are often caused by constipation, passing large or hard stools, or anal trauma.
The symptoms of hemorrhoids and anal fissures can be similar, but there are some differences. Hemorrhoids typically cause itching, burning, and bleeding, while anal fissures usually cause sharp pain during bowel movements and may also cause itching and bleeding. Hemorrhoids may also protrude from the anus, while anal fissures do not.
Both conditions can be treated with lifestyle modifications, such as dietary changes and increased water intake, as well as topical creams and medications. Severe cases may require medical procedures such as surgery or botox injections. It is important to consult a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
How can I contact gastroenterologist Dr. Zavos for an appointment?
Dr. Chris Zavos is a board-certified gastroenterologist and hepatologist, located in Thessaloniki Greece, and specifically in Kalamaria suburb, about 7 kilometres (4 miles) southeast of downtown Thessaloniki. His private office is at: Fanariou 8 street (near Aigaiou and Adrianoupoleos avenues), Kalamaria (Thessaloniki), Greece.
Thessaloniki International Airport is only 10 km away from his private office in Kalamaria and can be reached by taxi within 13 minutes from the airport.
Dr. Chris Zavos performs endoscopies at Bioclinic private hospital in downtown Thessaloniki (Mitropoleos 86 street).
You can contact Dr. Zavos at phone numbers: (+30)-6976596988 and (+30)-2311283833, or you can email him at czavos@ymail.com. Dr. Zavos responds to Greek and English languages.
References
- Cengiz TB, Gorgun E. Hemorrhoids: A range of treatments. Cleve Clin J Med 2019;86:612-620.
- Yamana T. Japanese Practice Guidelines for Anal Disorders I. Hemorrhoids. J Anus Rectum Colon 2018;1:89-99.
- Sandler RS, Peery AF. Rethinking What We Know About Hemorrhoids. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2019;17:8-15.
