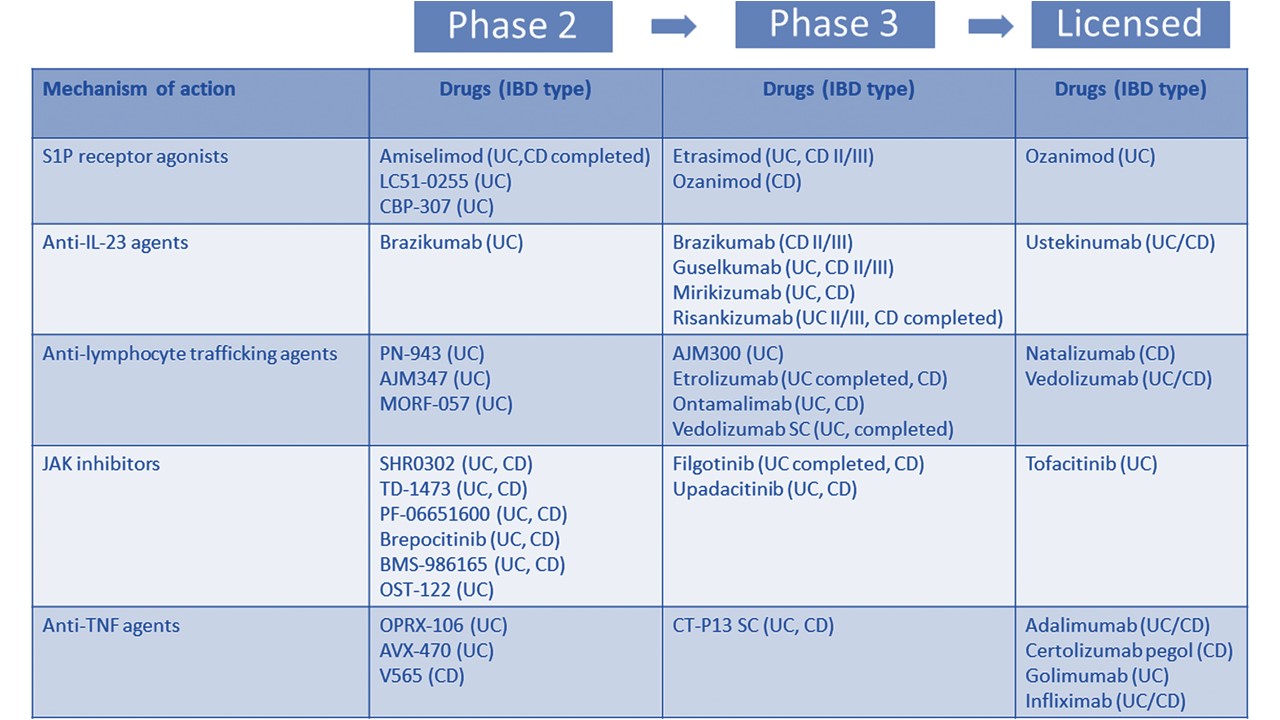
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) describes 2 conditions, i.e., Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC), characterized by chronic inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract. The present article includes the endpoints and conclusions of the most recent clinical trials on inflammatory bowel disease published in 2023 dating back until 2020. This article will be constantly updated to include the most recent clinical trials that will be published in a chronological order. You can click on the name of each study to move to the source of each published article. Dr. Christos Zavos is a board-certified gastroenterologist based in Thessaloniki, Greece.
2023
- LADI: Despite its effectiveness in treating Crohn’s disease, adalimumab is associated with an increased risk of infections and high health-care costs. We aimed to assess clinical outcomes of increased adalimumab dose intervals versus conventional dosing in patients with Crohn’s disease in stable remission. The study found that the individual benefit of increasing adalimumab dose intervals versus the risk of disease recurrence is a trade-off that should take patient preferences regarding medication and the risk of a flare into account.
2022
- LAUREL: We aimed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of etrolizumab for maintenance of remission in patients with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis. No significant differences were observed between maintenance etrolizumab and placebo in the primary endpoint of remission at week 62 among patients who had a clinical response at week 10. Etrolizumab was well tolerated in this population and no new safety signals were identified.
- HIBISCUS I and HIBISCUS II: The HIBISCUS studies aimed to compare the efficacy and safety of etrolizumab to adalimumab and placebo for induction of remission in patients with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis. Etrolizumab was superior to placebo for induction of remission in HIBISCUS I, but not in HIBISCUS II. Etrolizumab was well tolerated in both studies.
- STARDUST: Timely escalation of ustekinumab therapy for patients with Crohn’s disease, based on early endoscopic response, clinical symptoms, and biomarkers, did not result in significantly better endoscopic outcomes at week 48 than symptom-driven decisions alone. Future studies need to confirm if some subgroups of patient might benefit from a treat-to-target strategy with ustekinumab.
- TISKIDS: Study in newly diagnosed pediatric patients with moderate-to-severe Crohn’s disease (3–17 years old, weighted Pediatric CD Activity Index score [wPCDAI] >40). First-line infliximab was superior to conventional treatment in achieving short-term clinical and endoscopic remission, and had greater likelihood of maintaining clinical remission at week 52 on azathioprine monotherapy.
- SUSTAIN: Ustekinumab is effective and safe as short- and long-term treatment in a refractory cohort of CD patients in real-world clinical practice.
- GALAXI-1: Guselkumab, a selective p19 interleukin-23 antagonist, is approved for the treatment of plaque psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. This phase 2, double-blind, placebo-controlled study evaluated the efficacy and safety of guselkumab in patients with moderately to severely active Crohn’s disease with inadequate response or intolerance to conventional or biologic therapy. At week 12, all 3 dose regimens of guselkumab induced greater clinical and endoscopic improvements vs placebo, with a favorable safety profile.
- SEAVUE: Randomised, double-blind, parallel-group, active-comparator, phase 3b trial (SEAVUE) to evaluate the efficacy and safety of monotherapy with either ustekinumab or adalimumab in biologic-naive patients with moderately to severely active Crohn’s disease. Both ustekinumab and adalimumab monotherapies were highly effective in this population of biologic-naive patients, with no difference in the primary outcome between the drugs.
- SERENE UC (Study of a Novel Approach to Induction and Maintenance Dosing With Adalimumab in Patients With Moderate to Severe Ulcerative Colitis) evaluated the efficacy of higher adalimumab induction and maintenance dose regimens in patients with ulcerative colitis. Although primary end points were not met, a >10% absolute difference in clinical remission was demonstrated with higher adalimumab maintenance dosing. Higher dosing regimens were generally well tolerated and consistent with the known safety profile of adalimumab in ulcerative colitis.
- REMSWITCH: We assessed the effectiveness of switching from intravenous to subcutaneous infliximab in patients with inflammatory bowel diseases (IBDs) treated with or without intensified intravenous regimen. Switching from intravenous to subcutaneous infliximab 120 mg every other week is safe and well accepted, leading to a low risk of relapse in IBD patients except for those receiving 10 mg/kg every 4 weeks requiring 240 mg every other week.
- COMBO-MESA: Corticosteroids are the mainstay of treatment for hospitalized patients with acute severe ulcerative colitis (ASUC). However, whether the addition/continuation of mesalamine with corticosteroids during hospitalization is superior to corticosteroids alone is unknown. In this randomized controlled trial, combination of mesalamine with corticosteroids did not benefit hospitalized patients with ASUC more than corticosteroids alone. An exploratory signal for a reduced need for biologics at 90 days in the mesalamine group merits further evaluation.
- CRAFT-UC: We evaluated whether integration of novel diets for donors and patients, in addition to faecal transplantation (FT), could increase FT remission rate in refractory ulcerative colitis (UC). UC Exclusion Diet alone appeared to achieve higher clinical remission and mucosal healing than single donor FT with or without diet. The study was stopped for futility by a safety monitoring board.
- STOP-IT: Whether infliximab therapy can be successfully discontinued after patients with Crohn’s disease have attained sustained, clinical, biochemical, and endoscopic remission is unknown. Discontinuation of infliximab for patients with Crohn’s disease receiving long-term infliximab therapy and in clinical, biochemical, and endoscopic remission leads to a considerable risk of relapse.
- VISIBLE 2: Randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial evaluating a new subcutaneous [SC] vedolizumab formulation as maintenance treatment in adults with moderately to severely active Crohn’s disease [CD]. Vedolizumab SC is an effective and safe maintenance therapy in patients with CD who responded to two infusions of vedolizumab intravenous induction therapy.
- ERIca: Barrier healing is associated with decreased risk of disease progression in patients with clinically remittent IBD, with superior predictive performance compared with endoscopic and histologic remission. Analysis of barrier function might be considered as a future treatment target in clinical trials.
- ENTERPRISE: Randomized, double-blind, phase 4 trial evaluating 2 vedolizumab intravenous dosing regimens in patients with fistulizing CD (vedolizumab 300 mg intravenously at weeks 0, 2, 6, 14, and 22 vs. the same regimen plus an additional vedolizumab dose at week 10). Sustained improvements in fistulizing CD were seen with both vedolizumab regimens. An additional dose at week 10 does not appear to alter treatment outcomes. Safety profile was consistent with other vedolizumab studies.
- ADVANCE and MOTIVATE: ADVANCE and MOTIVATE were randomised, double-masked, placebo-controlled, phase 3 induction studies. Risankizumab, an interleukin (IL)-23 p19 inhibitor, was evaluated for safety and efficacy as induction therapy in patients with moderately to severely active Crohn’s disease. Risankizumab was effective and well tolerated as induction therapy in patients with moderately to severely active Crohn’s disease.
- TOUR: Tofacitinib is an oral, small-molecule JAK inhibitor for the treatment of ulcerative colitis (UC). Using a novel electronic reporting tool, we aimed to prospectively describe the onset of tofacitinib efficacy during induction therapy in a real-world study. In this prospective real-world study, tofacitinib resulted in a rapid and persistent improvement in UC disease activity patient-reported outcome data. The safety findings were consistent with the established safety profile of tofacitinib.
- VIP: We sought to determine whether COVID-19 vaccine-induced antibody responses were altered in patients with IBD on commonly used immunosuppressive drugs. For patients with IBD, the immunogenicity of COVID-19 vaccines varies according to immunosuppressive drug exposure, and is attenuated in recipients of infliximab, infliximab plus thiopurines, and tofacitinib. Scheduling of third primary, or booster, doses could be personalised on the basis of an individual’s treatment, and patients taking anti-tumour necrosis factor and tofacitinib should be prioritised.
- AJM300: AJM300 is an oral, small-molecule α4-integrin antagonist. We assessed the efficacy and safety of AJM300 in patients with moderately active ulcerative colitis. AJM300 was well tolerated and induced a clinical response in patients with moderately active ulcerative colitis who had an inadequate response or intolerance to mesalazine. AJM300 could be a novel induction therapy for the treatment of patients with moderately active ulcerative colitis.
- FORTIFY is a phase 3, multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, maintenance withdrawal study that enrolled participants with clinical response to risankizumab in the ADVANCE or MOTIVATE induction studies. Patients in ADVANCE or MOTIVATE were aged 16–80 years with moderately to severely active Crohn’s disease. We report the efficacy and safety of subcutaneous risankizumab as maintenance therapy.
- HUBBLE is a dose-ranging, phase 2 trial evaluating the pharmacokinetic, safety and efficacy of intravenous vedolizumab for paediatric IBD. Vedolizumab exposure increased in an approximate dose-proportional manner. No clear dose–response relationship was observed in this limited cohort. No new safety signals were identified.
- PUCCINI: Whether preoperative treatment of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) with tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFis) increases the risk of postoperative infectious complications remains controversial. The primary aim of this study was to determine whether preoperative exposure to TNFis is an independent risk factor for postoperative infectious complications within 30 days of surgery. Preoperative TNFi exposure was not associated with postoperative infectious complications in a large prospective multicenter cohort.
- PISA-II: Multicenter study that assessed radiological healing in patients who received short-term anti-TNF treatment and surgical closure compared with those who received anti-TNF treatment alone. Short-term anti-TNF treatment combined with surgical closure induces long-term MRI healing more frequently than anti-TNF therapy in patients with Crohn’s perianal fistulas. These data suggest that patients with Crohn’s perianal fistula amenable for surgical closure should be counselled for this therapeutic approach.
2021
- SELECTION: Phase 2b/3, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled trial that assessed the efficacy and safety of filgotinib, a once-daily, oral Janus kinase 1 preferential inhibitor, for treatment of ulcerative colitis. Filgotinib 200 mg was well tolerated, and efficacious in inducing and maintaining clinical remission compared with placebo in patients with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis.
- HICKORY is a multicentre, phase 3, double-blind, placebo-controlled study in adult (18–80 years) patients with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis that evaluated the efficacy and safety of etrolizumab in patients with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis who had been previously treated with anti-tumour necrosis factor (TNF) agents. HICKORY demonstrated that a significantly higher proportion of patients with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis who had been previously treated with anti-TNF agent were able to achieve remission at week 14 when treated with etrolizumab compared with placebo; however, there was no significant difference between groups in remission at week 66 among patients with a clinical response at week 14.
- EEN: Open-label randomised controlled trial that investigated the effectiveness of exclusive enteral nutrition (EEN) as adjunctive therapy to intravenous corticosteroids in patients with acute severe ulcerative colitis (ASUC). EEN for 7 days may augment corticosteroid responsiveness in patients with ASUC.
- TRUE NORTH: Ozanimod, a selective sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor modulator, is under investigation for the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. We conducted a phase 3, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of ozanimod as induction and maintenance therapy in patients with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis. Ozanimod was more effective than placebo as induction and maintenance therapy in patients with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis.
- DINE-CD: This study compared the effectiveness of the Specific Carbohydrate Diet (SCD) to the Mediterranean diet (MD) as treatment for Crohn’s disease (CD) with mild to moderate symptoms. The SCD was not superior to the MD to achieve symptomatic remission, fecal calprotectin response, and CRP response. CRP response was uncommon. Given these results, the greater ease of following the MD and other health benefits associated with the MD, the MD may be preferred to the SCD for most patients with CD with mild to moderate symptoms.
- GARDENIA: Randomised, double-blind, double-dummy, parallel-group, phase 3 study that compared the safety and efficacy of etrolizumab with infliximab in patients with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis. Although the study did not show statistical superiority for the primary endpoint, etrolizumab performed similarly to infliximab from a clinical viewpoint.
- CLARITY: Infliximab is associated with attenuated serological responses to SARS-CoV-2 that were further blunted by immunomodulators used as concomitant therapy. Impaired serological responses to SARS-CoV-2 infection might have important implications for global public health policy and individual anti-TNF-treated patients. Serological testing and virus surveillance should be considered to detect suboptimal vaccine responses, persistent infection and viral evolution to inform public health policy.
- UNISTAR: Phase 1, multicentre, 16-week, double-blind, induction dose-ranging study that evaluated the pharmacokinetics, safety/tolerability, and efficacy of ustekinumab in children with moderately to severely active Crohn’s disease. The pharmacokinetics/safety profiles were generally consistent with those observed in adults with Crohn’s disease. These results suggest a different dosing regimen may be required for patients <40 kg from that employed in this study; additional pharmacokinetic analyses may be needed in this population.
- TOUCHSTONE OLE: This analysis examined the long-term safety and efficacy of ozanimod in patients with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis [UC] with ≥ 4 years of follow-up in the phase 2 TOUCHSTONE open-label extension [OLE]. There was a high rate of continued study participation and long-term benefit with ozanimod HCl 1 mg daily based on clinical, histological and biomarker measures in patients with moderately to severely active UC in the TOUCHSTONE OLE.
- OASIS OLE: Etrasimod is an oral, selective, sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor modulator. In a phase 2, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in adults with moderately-to-severely active ulcerative colitis [OASIS], etrasimod 2 mg provided significant benefit versus placebo and was generally well tolerated. This open-label extension [OLE] evaluated safety and efficacy of etrasimod for up to 52 weeks. In this long-term extension study, etrasimod 2 mg demonstrated a favourable safety profile. Most patients with clinical response, clinical remission, or endoscopic improvement at Week 12 maintained that status to end of treatment.
- ENVISION I: The aim of this study was to assess the safety and efficacy of adalimumab in children with moderate-to-severe ulcerative colitis. Clinically meaningful rates of remission and response were reported in children who received adalimumab in this study. No new safety signals were observed, suggesting that adalimumab is an efficacious and safe treatment option for children with moderate-to-severe ulcerative colitis.
- STRIDENT: Strictures are the most common structural complication of Crohn’s disease. Surgery and endoscopic balloon dilation are the main treatments; drug therapy has been considered contraindicated. Given that most strictures have an inflammatory component, we aimed to find out whether strictures are responsive to drug treatment and whether intensive drug therapy is more effective than standard drug therapy. The study found that Crohn’s disease strictures are responsive to drug treatment. Most patients had improved symptoms and stricture morphology. Treat-to-target therapy intensification resulted in less treatment failure, a reduction in stricture-associated inflammation, and greater improvement in stricture morphology, although these differences were not significantly different from standard therapy.
- FUTURE: 12-week, open-label, prospective phase 2a trial. Inhibition of interleukin (IL)-6 appears to be effective, but the therapeutic benefit of a complete IL6/IL6 receptor (IL6R) blockade is limited by profound immunosuppression. Evidence has emerged that chronic proinflammatory activity of IL6 is mainly mediated by trans-signaling via a complex of IL6 bound to soluble IL6R engaging the gp130 co-receptor without the need for membrane-bound IL6R. We have developed a decoy protein, sgp130Fc, that exclusively blocks IL6 proinflammatory trans-signaling and has shown efficacy in preclinical models of IBD, without signs of immunosuppression. Our data suggest that blockade of IL6 trans-signaling holds great promise for the therapy of IBD and should undergo full clinical development as a new immunoregulatory therapy for IBD.
- RIVETING: Tofacitinib is an oral, small molecule Janus kinase inhibitor for the treatment of ulcerative colitis. We present primary completion analysis from RIVETING, an ongoing, double-blind, randomised, parallel-group trial evaluating efficacy and safety of tofacitinib dose reduction to 5 mg twice daily [BID] versus remaining on 10 mg BID in patients in stable remission on tofacitinib 10 mg BID maintenance therapy. The study found that most patients in stable remission on 10 mg BID maintenance therapy maintained remission following dose de-escalation. For patients who dose de-escalated, those in deep endoscopic remission and those without prior tumour necrosis factor inhibitor failure were more likely to maintain remission. Efficacy data were limited to the first 6 months; a longer duration of follow-up during RIVETING will further characterise the impact of dose reduction on maintenance of remission. Safety findings were consistent with the established safety profile of tofacitinib.
2020
- VISIBLE 1: Subcutaneous vedolizumab is effective as maintenance therapy in patients with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis who had a clinical response to intravenous vedolizumab induction therapy. It has a favorable safety and tolerability profile.
- CELEST: Double-blind, phase 2 trial in adults with moderate to severe CD and inadequate response or intolerance to immunosuppressants or tumor necrosis factor antagonists that evaluated the efficacy and safety of upadacitinib, an oral selective Janus kinase 1 inhibitor. The study found that upadacitinib induced endoscopic remission in a significant proportion of patients compared with placebo. Upadacitinib’s benefit/risk profile supports further development for treatment of CD.
- U-ACHIEVE: Multicenter, double-blind, phase 2b study of 250 adults with moderately to severely active UC and an inadequate response, loss of response, or intolerance to corticosteroids, immunosuppressive agents, and/or biologic therapies, that evaluated the efficacy and safety of upadacitinib, an oral selective inhibitor of Janus kinase 1, as induction therapy for ulcerative colitis. The study found that upadacitinib was more effective than placebo for inducing remission in patients with moderately to severely active UC.
- CONCEIVE: Study on outcome of vedolizumab-exposed (VDZE) pregnancies showing that no new safety signal was detected in VDZE pregnancies although larger, prospective studies are required for confirmation.
- PISA-I: The aim of this study was to assess if chronic seton drainage for patients with perianal Crohn’s disease fistulas would result in less re-interventions, compared with anti-TNF and compared with surgical closure. The study was stopped by the data safety monitoring board because of futility. Seton treatment was associated with the highest re-intervention rate. The results imply that chronic seton treatment should not be recommended as the sole treatment for perianal Crohn’s fistulas.
- STEPSTONE: We aimed to evaluate the effects of ozanimod, an oral agent selectively targeting sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor subtypes 1 and 5, on endoscopic disease activity in Crohn’s disease. Endoscopic, histological, and clinical improvements were seen within 12 weeks of initiating ozanimod therapy in patients with moderately to severely active Crohn’s disease. Phase 3 placebo-controlled trials have been initiated.
- CONDUCT: Cobitolimod is a topically administered, DNA-based oligonucleotide that activates Toll-like receptor 9 (TLR9), and previous research has shown clinical efficacy in patients with moderate-to-severe ulcerative colitis. In this randomised, double-blind, five-arm, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging phase 2b study, we assessed the efficacy and safety of different dose regimens of cobitolimod for induction therapy in patients with moderate-to-severe, left-sided ulcerative colitis. Two topical administrations of cobitolimod 250 mg were well tolerated and more effective than placebo in inducing clinical remission 6 weeks after the start of treatment. TLR9 activation is a promising novel therapeutic target in ulcerative colitis and warrants further testing, with phase 3 trials of cobitolimod planned.
- OASIS: Etrasimod (APD334) is an oral, selective sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor modulator in development for immune-mediated inflammatory disorders. We assessed the efficacy and safety of etrasimod in patients with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis (UC). In this phase 2, proof-of-concept, double-blind, parallel-group study in patients with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis, etrasimod 2 mg was more effective than placebo in producing clinical and endoscopic improvements. Further clinical development is warranted.
- PIANO: Pregnant women with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) may require biologic or thiopurine therapy to control disease activity. Lack of safety data has led to therapy discontinuation during pregnancy, with health repercussions to mother and child. Biologic, thiopurine, or combination therapy exposure during pregnancy was not associated with increased adverse maternal or fetal outcomes at birth or in the first year of life. Therapy with these agents can be continued throughout pregnancy in women with IBD to maintain disease control and reduce pregnancy-related adverse events.
- I6T-MC-AMAC: We investigated the effects of mirikizumab, a monoclonal antibody against the p19 subunit of interleukin 23, in a phase 2 study of patients with UC. The study found that mirikizumab was effective in inducing a clinical response after 12 weeks. Additional studies are required to determine the optimal dose for induction of remission. Mirikizumab showed durable efficacy throughout the maintenance period.
- PRASCO: Patients with acute severe colitis have alterations in the microbiome characterized by loss of diversity and presence of predominant bacterial species. Quadruple therapy (amoxicillin, vancomycin, metronidazole, doxycycline/ciprofloxacin) in addition to intravenous-corticosteroids improved disease activity on day 5, but larger studies are needed to determine whether this is associated with improved long-term outcomes.
