What are probiotics?
Probiotics are live microorganisms that are beneficial to human health, especially in relation to the digestive system. They are found naturally in certain foods and supplements, and can also be added to some foods. Probiotics are often referred to as “good” bacteria because they help maintain a healthy balance of bacteria in the gut. They are believed to support the immune system, promote healthy digestion, and may even have a positive impact on mental health. Common types of probiotics include lactobacillus and bifidobacterium, among others.
Are there different strains of probiotics?
There are many different probiotic strains, each with unique characteristics and potential health benefits. Here are some of the most commonly studied probiotic strains:
- Lactobacillus acidophilus
- Lactobacillus casei
- Lactobacillus rhamnosus
- Bifidobacterium bifidum
- Bifidobacterium lactis
- Bifidobacterium longum
- Streptococcus thermophilus
- Saccharomyces boulardii
- Lactococcus lactis
- Escherichia coli Nissle 1917
Each strain of probiotics has unique benefits and characteristics. For example, Lactobacillus acidophilus is commonly found in the vagina and may help prevent vaginal infections. Bifidobacterium lactis has been shown to improve digestion and reduce inflammation. Saccharomyces boulardii is a type of yeast that may help prevent diarrhea caused by antibiotics.
When choosing a probiotic supplement, it’s important to consider the specific strains and their potential benefits for your health needs. Different strains may be more effective for certain health concerns than others. Also, choose a reputable brand and follow the recommended dosage instructions.
What are the benefits of taking probiotics?
There are several potential benefits of taking probiotics, including:
- Improving digestion and nutrient absorption: Probiotics help break down food and extract nutrients from it, which can aid in digestion and nutrient absorption.
- Boosting the immune system: Probiotics have been shown to support the immune system by promoting the production of antibodies and improving the function of immune cells.
- Reducing the risk of certain infections: Probiotics may help prevent or reduce the severity of some infections, including urinary tract infections and respiratory infections.
- Alleviating digestive issues: Probiotics have been shown to help alleviate symptoms of digestive issues such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and diarrhea caused by infections or antibiotic use.
- Improving mental health: Some research suggests that probiotics may have a positive impact on mental health by reducing symptoms of anxiety and depression.
What are some common myths surrounding probiotics?
There are several common myths surrounding probiotics. Here are a few examples:
- All probiotics are the same: This is not true. Different strains of probiotics have different characteristics and potential health benefits. It is important to choose the right probiotic strain for your specific health needs.
- Probiotics are only for digestive health: While probiotics are often associated with digestive health, they may also have benefits for other aspects of health, such as immune function, mood, and skin health.
- Probiotics are a cure-all: While probiotics can be beneficial for certain health concerns, they are not a cure-all for all health problems. It is important to use probiotics as part of a comprehensive approach to health that includes a healthy diet, exercise, and other lifestyle factors.
- More is always better: Taking high doses of probiotics may not necessarily be beneficial, and in some cases, may even be harmful. It is important to follow the recommended dosage instructions for any probiotic supplement.
- All probiotics are safe: While probiotics are generally considered safe, some people may experience side effects such as bloating, gas, or diarrhea. It is important to talk to your healthcare provider before taking probiotics, especially if you have any underlying health conditions or are taking medications.
One should separate fact from fiction when it comes to probiotics. By understanding the potential benefits and limitations of probiotics, you can make informed decisions about whether they may be helpful for your health needs.
Which infections may probiotics help?
Probiotics may be helpful for certain types of infections, especially those related to the digestive system. Here are some examples of infections that probiotics may be indicated for:
- Antibiotic-associated diarrhea: Probiotics may help prevent or treat diarrhea that is caused by taking antibiotics, including Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy, which can disrupt the natural balance of bacteria in the gut.
- Clostridioides difficile infection (CDI): CDI is a type of bacterial infection that can cause severe diarrhea and inflammation of the colon. Probiotics may help reduce the risk of CDI or improve outcomes in people who have already developed the infection.
- Vaginal infections: Certain strains of probiotics, such as Lactobacillus crispatus and Lactobacillus jensenii, may help prevent or treat bacterial vaginosis and yeast infections in women.
- Upper respiratory tract infections: Some studies have suggested that probiotics may help reduce the severity and duration of symptoms of common colds and other upper respiratory tract infections.
Probiotics should not be used as a substitute for appropriate medical treatment for infections.
What are the best probiotic supplements?
The best probiotic supplements may vary depending on individual needs and health conditions. Here are some factors to consider when choosing a probiotic supplement:
- Strain diversity: Look for a supplement that contains multiple strains of probiotics, as different strains have different benefits.
- Colony-forming units (CFUs): The CFUs indicate the number of live bacteria in the supplement. Generally, a higher CFU count is better, but the specific amount needed may vary depending on individual needs.
- Shelf stability: Choose a supplement that has been tested for shelf stability to ensure that the bacteria remain alive and effective until the expiration date.
- Quality and purity: Look for a supplement that has been third-party tested to ensure quality and purity.
- Price and brand reputation: Consider the cost of the supplement and the reputation of the brand.
What are the side effects of probiotics?
Probiotics are generally considered safe for most people, but in some cases, they may cause mild side effects such as:
- Digestive discomfort: Some people may experience bloating, gas, or mild stomach upset when first starting to take probiotics.
- Allergic reactions: People with a history of allergies or sensitivities to certain foods or substances may be at risk of an allergic reaction to probiotics.
- Infection risk: In rare cases, probiotics may cause infections, particularly in people with weakened immune systems or those with catheters or other medical devices.
- Interaction with medications: Probiotics may interact with some medications, including antibiotics, immunosuppressants, and some chemotherapy drugs.
- Risk for people with certain health conditions: People with certain health conditions, such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) or a history of pancreatitis, may need to avoid or limit probiotic use.
How do probiotics work?
Probiotics work in several ways to support human health. Here are some of the main ways that probiotics work:
- Supporting gut health: Probiotics help maintain a healthy balance of “good” and “bad” bacteria in the gut. This can help prevent the growth of harmful bacteria and promote healthy digestion.
- Enhancing the immune system: Probiotics help stimulate the production of antibodies and other immune system cells, which can help protect against infections and other diseases.
- Producing beneficial compounds: Probiotics can produce compounds such as short-chain fatty acids that help support the health of the gut lining and may have other health benefits.
- Reducing inflammation: Some research suggests that probiotics may help reduce inflammation in the body, which is believed to be a factor in the development of several chronic diseases.
- Modulating neurotransmitters: Certain probiotics may produce neurotransmitters such as serotonin and dopamine, which can have a positive impact on mental health.
Different strains of probiotics may work differently, and the specific benefits of probiotics may vary depending on individual needs and health conditions. Additionally, more research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms by which probiotics work and their impact on human health.
What foods contain probiotics?
There are several foods that naturally contain probiotics, including:
- Yogurt: Yogurt is one of the most well-known sources of probiotics. Look for yogurt that contains live and active cultures.
- Kefir: Kefir is a fermented milk drink that contains a variety of probiotics.
- Sauerkraut: Sauerkraut is made from fermented cabbage and is a good source of probiotics.
- Kimchi: Kimchi is a Korean dish made from fermented vegetables, typically cabbage or radish.
- Miso: Miso is a traditional Japanese seasoning made from fermented soybeans and other grains.
- Tempeh: Tempeh is a type of fermented soybean cake that is often used as a meat substitute.
- Kombucha: Kombucha is a fermented tea drink that is often infused with fruit or herbs.
- Pickles: Pickles that have been naturally fermented (not pickled in vinegar) can be a good source of probiotics.
The amount and variety of probiotics in these foods can vary depending on the specific product and the fermentation process used. Additionally, some of these foods may be high in sodium or added sugars, so it is important to choose options that fit within a balanced and healthy diet.
Can probiotics help with digestive issues?
Probiotics help to balance the bacteria in the gut microbiome, which can become imbalanced due to factors such as antibiotics, diet, and stress. This imbalance can lead to digestive issues such as diarrhea, constipation, bloating, and gas. By introducing beneficial bacteria into the gut, probiotics can help to restore balance and improve digestive function.
Research has shown that probiotics can be effective in treating conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and antibiotic-associated diarrhea. However, the effectiveness of probiotics can vary depending on the specific strain used, the dosage, and the individual’s gut microbiome.
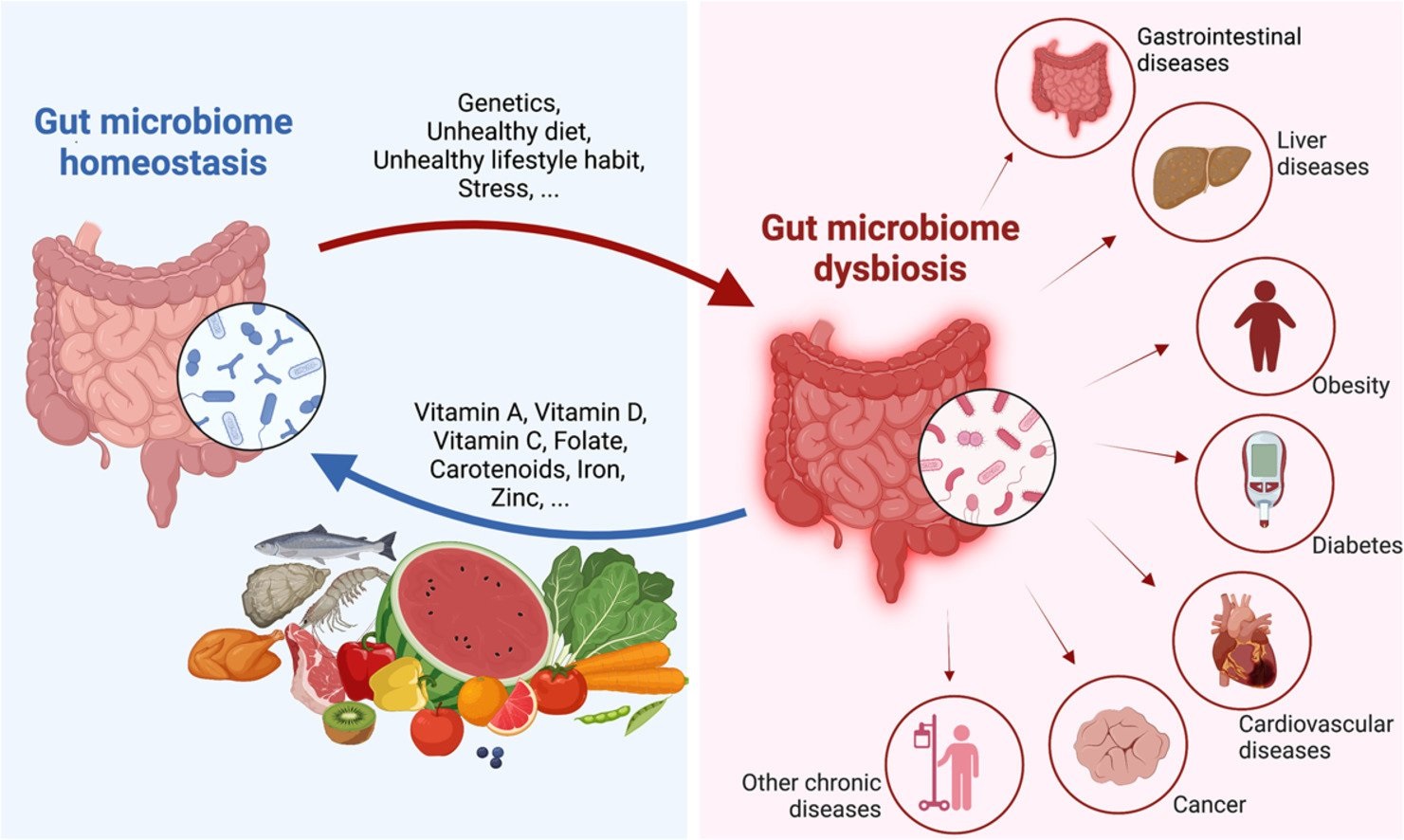
Can probiotics help with weight loss?
The evidence on whether probiotics can help with weight loss is mixed, and more research is needed to fully understand their potential effects. Most of the studies have found no significant effects of probiotics on weight loss. The overall evidence is limited by a lack of consistent findings, small study sizes, and variation in the types and doses of probiotics used.
Probiotics alone are not a magic solution for weight loss. To achieve and maintain a healthy weight, it’s important to follow a balanced diet and engage in regular physical activity. However, incorporating probiotics into a healthy lifestyle may offer some additional benefits.
Are probiotics safe for children?
Probiotics can be safe for children, but it is important to talk to your child’s healthcare provider before giving them probiotics, especially if your child has any underlying health conditions or is taking any medications.
In general, probiotics are considered safe for healthy children. They are naturally found in some foods, such as yogurt and kefir, and can also be taken in supplement form. Probiotics can help support children’s digestive health and immune function.
However, some children may experience side effects from probiotics, such as bloating, gas, or diarrhea. These side effects are generally mild and go away on their own after a few days. If your child experiences severe or persistent symptoms, stop giving them the probiotics and talk to their healthcare provider.
Choose the right probiotic for your child’s needs. The specific strains and dosages of probiotics that are effective for adults may not be appropriate for children. Talk to your child’s pediatrician to determine the best probiotic for your child’s age and health needs.
How long do you need to take probiotics for them to work?
The length of time it takes for probiotics to work can vary depending on the individual and the specific health concern being addressed.
For some digestive issues, such as antibiotic-associated diarrhea, probiotics may start working within a few days. However, for other conditions, such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), it may take several weeks or even a couple of months to see improvements.
Probiotics are not a quick fix and may not work for everyone. The effectiveness of probiotics can vary depending on the specific strain used, the dosage, and the individual’s gut microbiome.
How can I contact gastroenterologist Dr. Zavos for an appointment?
Dr. Chris Zavos is a board-certified gastroenterologist and hepatologist, located in Thessaloniki Greece, and specifically in Kalamaria suburb, about 7 kilometres (4 miles) southeast of downtown Thessaloniki. His private office is at: Fanariou 8 street (near Aigaiou and Adrianoupoleos avenues), Kalamaria (Thessaloniki), Greece.
Thessaloniki International Airport is only 10 km away from his private office in Kalamaria and can be reached by taxi within 13 minutes from the airport.
Dr. Chris Zavos performs endoscopies at Bioclinic private hospital in downtown Thessaloniki (Mitropoleos 86 street).
You can contact Dr. Zavos at phone numbers: (+30)-6976596988 and (+30)-2311283833, or you can email him at czavos@ymail.com. Dr. Zavos responds to Greek and English languages.
References
- Sipsas NV, Zonios DI, Kordossis T. Safety of Lactobacillus strains used as probiotic agents. Clin Infect Dis 2002;34:1283-4; author reply 1284-5.
- Chang L, Sultan S, et al. AGA Clinical Practice Guideline on the Pharmacological Management of Irritable Bowel Syndrome With Constipation. Gastroenterology 2022 Jul;163(1):118-36.
- Lembo A, Sultan S, et al. AGA Clinical Practice Guideline on the Pharmacological Management of Irritable Bowel Syndrome With Diarrhea. Gastroenterology 2022 Jul;163(1):137-51.
- Lee JY, Tsolis RM, Bäumler AJ. The microbiome and gut homeostasis. Science 2022 Jul;377:eabp9960.
