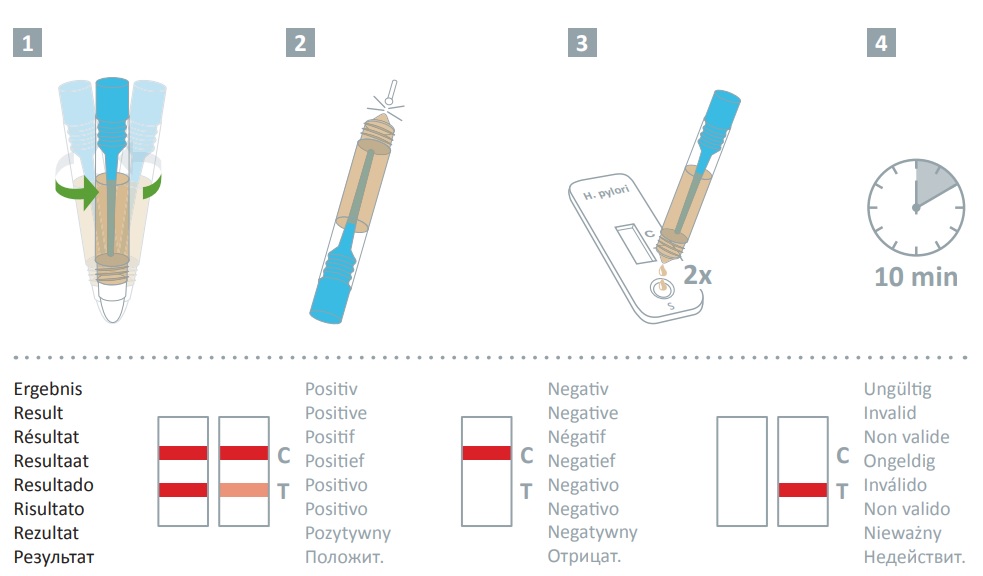
Helicobacter pylori stool antigen test: Procedure
- Ensure tests, specimens, buffer, and/or controls are at room temperature (15-30°C) prior to testing.
Specimen Collection and Pre-treatment:
- Using Specimen Dilution Tubes:
- Utilize the specimen dilution tubes provided in the test kit for collection.
- Aim to perform the assay within 6 hours after collection for best results.
- Specimen Handling:
- Remove the dilution tube applicator carefully to avoid spilling or splattering.
- Collect specimens by inserting the applicator stick into at least three different sites of the feces to gather approximately 50 mg (equivalent to 1/4 of a pea).
- Reinsert the applicator into the tube and securely tighten the cap, ensuring not to break the tip of the tube.
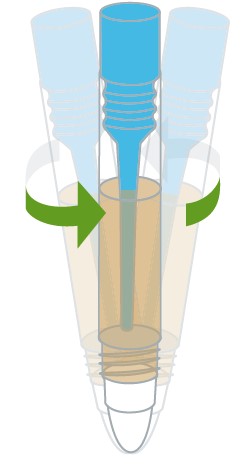
- Vigorously shake the specimen dilution tube to mix the specimen with the extraction buffer.
Testing Procedure:
- Test Setup:
- Remove the H. pylori Ag test cassette from its sealed pouch and place it on a clean, level surface.
- Label the test cassette with patient or control identification.
- Perform the assay within one hour for optimal results.
- Specimen Application:
- Use a tissue paper to break the tip of the dilution tube.
- Hold the tube vertically and dispense 2 drops of the solution into the specimen well (S) of the test cassette, avoiding air bubbles and not allowing the solution to enter the result window.
- Observation and Results:
- Observe as the test operates and color moves along the membrane.
- Read the result at 10 minutes; do not interpret results after 20 minutes.
Note:
- If the specimen does not migrate due to the presence of particles, centrifuge the extracted specimens. Collect 80 µL of the supernatant, dispense it into the specimen well (S) of a new test cassette, and repeat the testing instructions.
Helicobacter pylori stool antigen test: Result interpretation
Positive:
- Two colored lines appear on the membrane.
- One line appears in the control line region (C).
- Another line appears in the test line region (T).
- Two colored lines appear on the membrane.
Negative:
- Only one colored line appears.
- This line is in the control line region (C).
- No colored line appears in the test line region (T).
- Only one colored line appears.
Invalid:
- No control line appears.
- Tests without a control line at the specified reading time are considered invalid and must be discarded.
- Review the procedure and repeat the test with a new test cassette.
- If the issue persists, stop using the kit and contact your distributor.
- No control line appears.
Note:
- The intensity of the color in the test line region (T) can vary depending on the concentration of analytes present in the specimen.
- Any shade of color in the test line region should be considered a positive result.
- This test is qualitative only and does not measure analyte concentration.
- Potential causes for control line failure include insufficient specimen volume, incorrect operating procedures, or expired tests.